Elementary Lesions
Micronodulation
Characteristics
Focal rounded opacities < 3 mm presenting the following characteristics:
Attenuation: ground glass opacity or tissular or even calcified
Borders: blurry to clear
Diagnostic Orientation
The location of micronodulations helps guide the diagnosis:
within the lungs
within the secondary pulmonary lobule: key to diagnosis
The CT scans helps categorise diffuse micronodulations based on three types of lobular distribution, thereby significantly reducing the differential diagnosis:
random micronodulation
centrilobular micronodulation
centrilobular micronodulation
1. Micronodulation, perilymphatic distribution
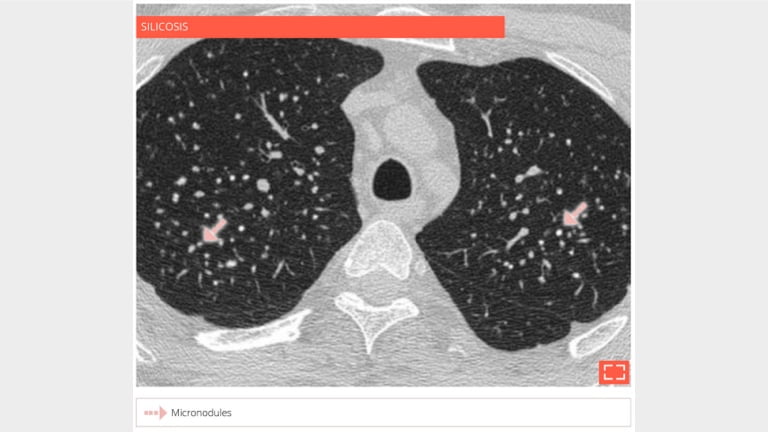
- Coal workers’ pneumoconiosis.
- Extensive micronodulation with a perilymphatic distribution. Micronodules have an apical and posterior predominance.
2. Micronodulation
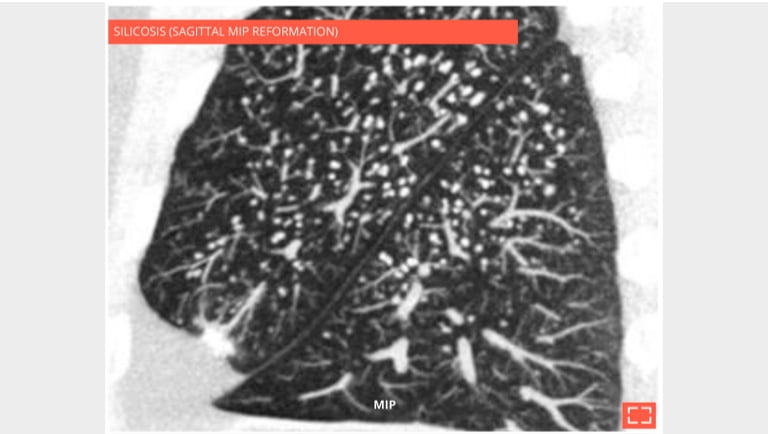
Centrilobular and perilymphatic micronodulation.
3. Micronodulation, centrilobular distribution
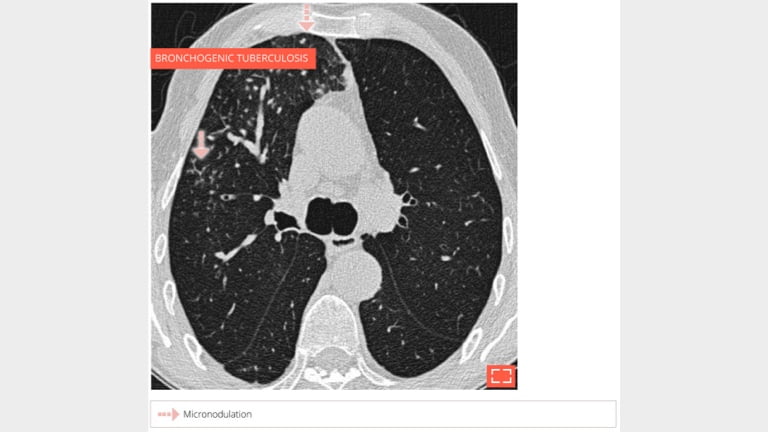
Micronodulation in the ventral segment of the right upper lobe sparing the subpleural part of the lung.
