Elementary Lesions
Honeycomb change
Definition
Irreversible terminal destruction of the lung (end stage)
Characteristics
Enlarged pulmonary alveolar cavities: clustered cystic airspaces
Thick, fibrous walls
At least partially lined by bronchiolar epithelium
Contents: mucin and/or inflammatory cells: neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes
Diagnostic Orientation
Location
lower lobes
Alveolar epithelium
Absent
sometimes replaced by bronchiolar epithelium when the adjacent bronchiolar lining slides in. This process is known as bronchial epithelial metaplasia.
1. Honeycomb change
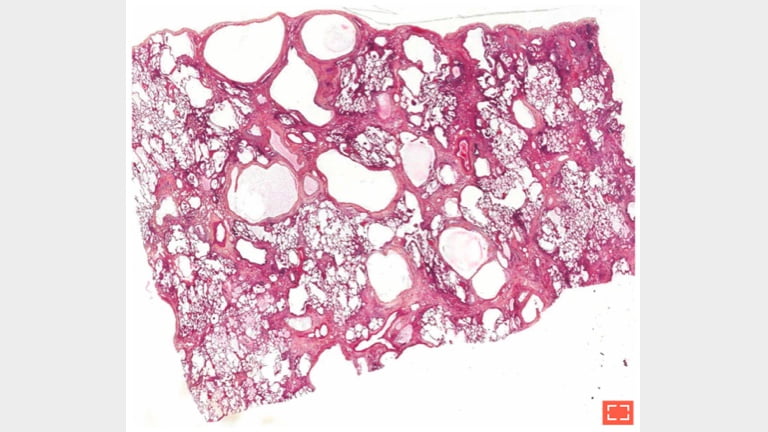
2. Subpleural honeycombing cysts
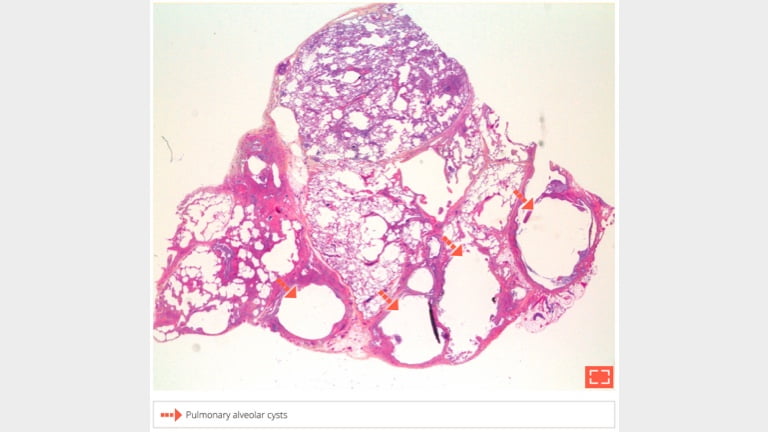
3. Mucin filled alveolar cysts delimited by thick fibrotic walls
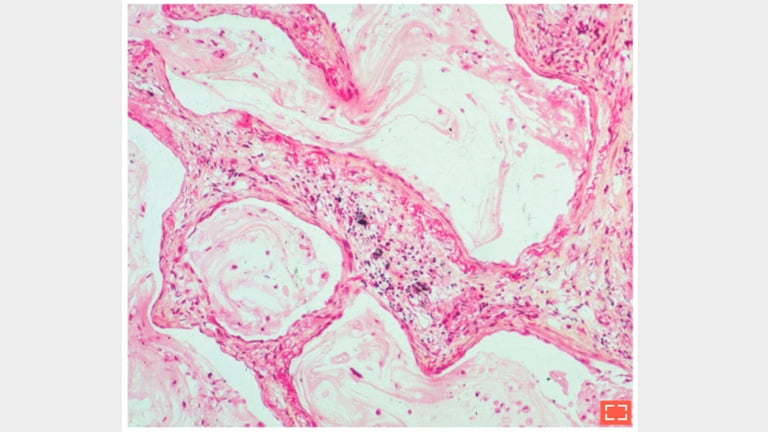
4. Alveolar cysts with thick fibrotic walls
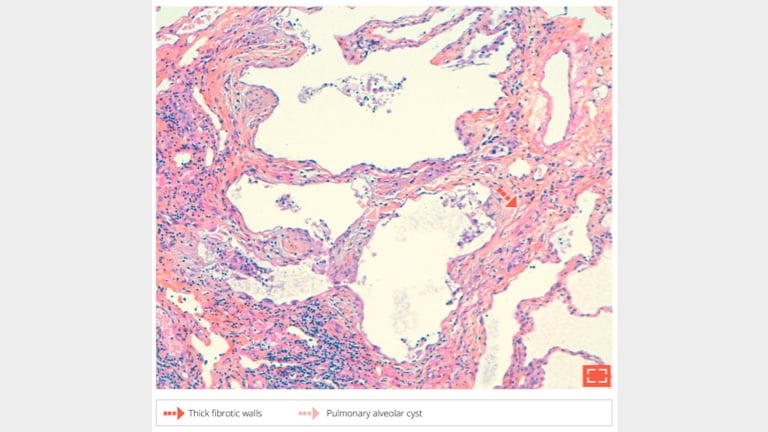
5. Mucin filled alveolar cysts
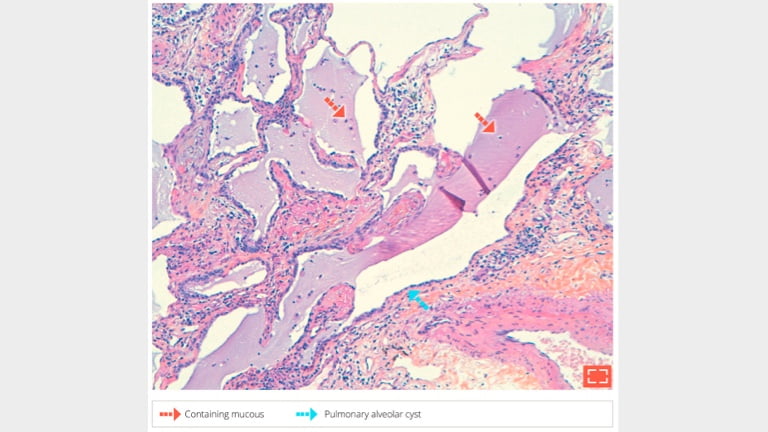
6. Honeycombing cysts
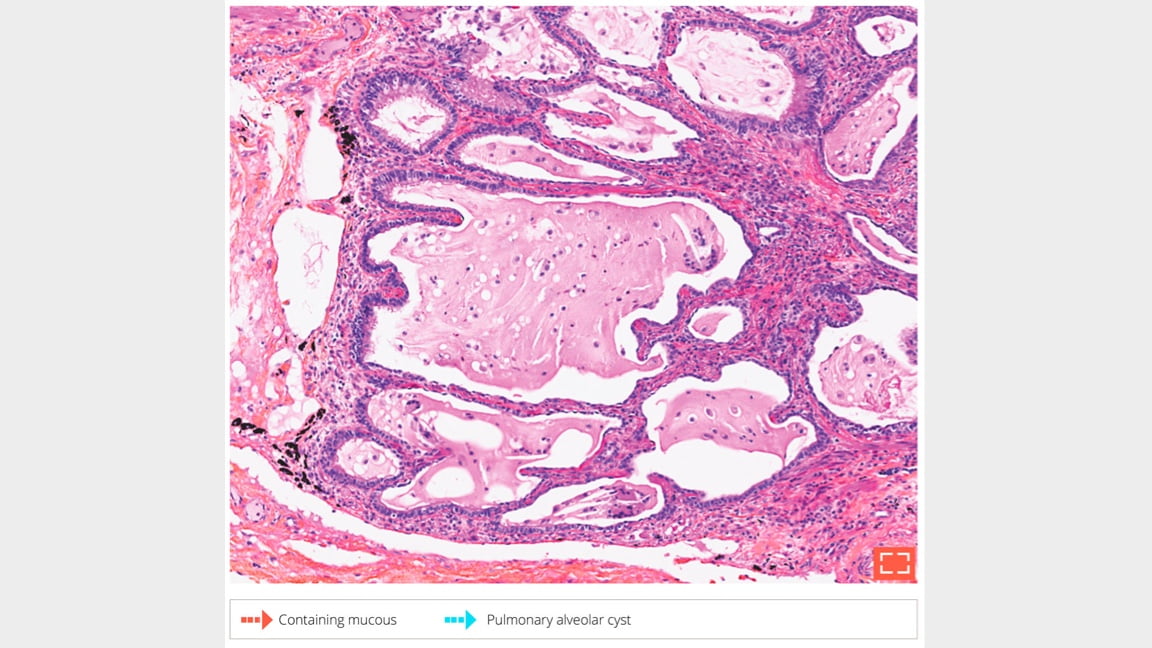
Intraluminal mucin containing inflammatory cells. Chronic lymphocytic inflammation in the alveolar walls.
7. Alveolar cysts
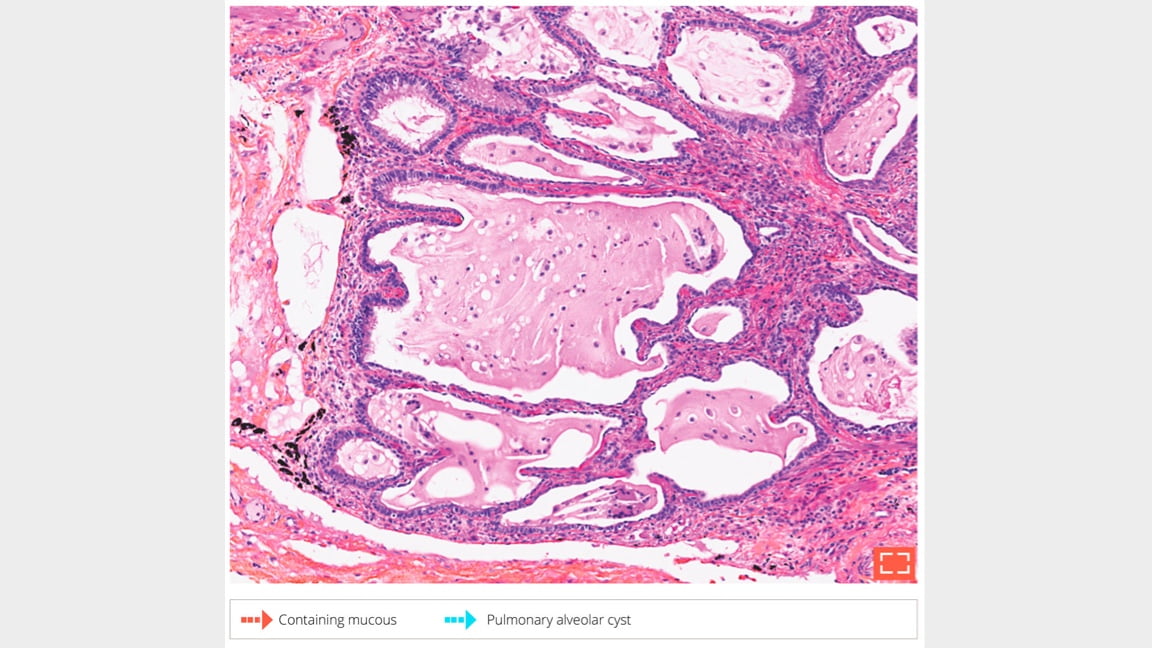
Pulmonary alveolar cyst partially lined by pseudo-stratified, ciliated respiratory epithelium.
