Elementary Lesions
Intralobular reticulations (lines)
Characteristics
Small linear or curved intralobular opacities measuring less than 10 mm forming an irregular reticulation
They can be isolated or associated with other signs
Diagnostic Orientation
If the intralobular reticulations are posterior and inferior subpleural reticulations
Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP, probable UIP, indeterminate for UIP, alternative diagnosis of UIP) / Connective tissue disease (CTD)
Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
Desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP)
If intralobular reticulations are associated with ground-glass opacity
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP), alveolar proteinosis
1. Intralobular reticulations associated with ground-glass opacity
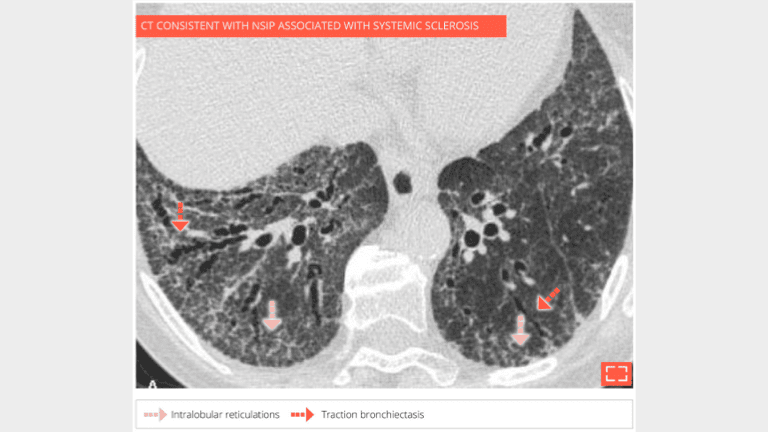
Diffuse ground-glass opacities in the lower posterior lungs with intralobular reticulations and traction bronchiectasis, no honeycombing.
2. Intralobular reticulations
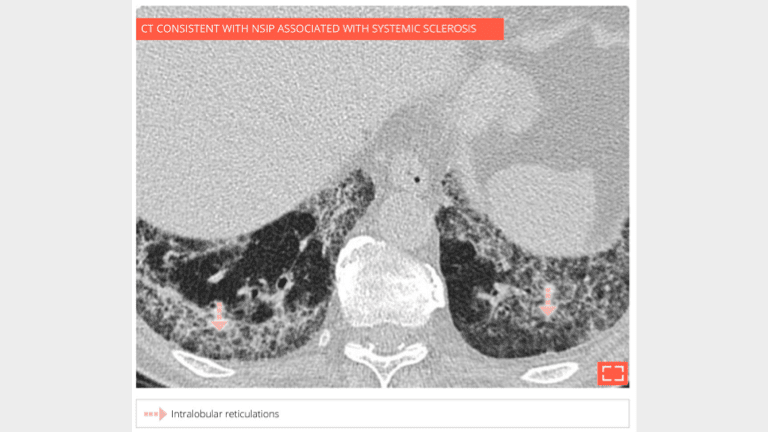
Marked intralobular reticulations in the 2 lung bases without honeycombing. Note the relative lung savings immediately under pleura, pointing to a NSIP.
3. Intralobular reticulations
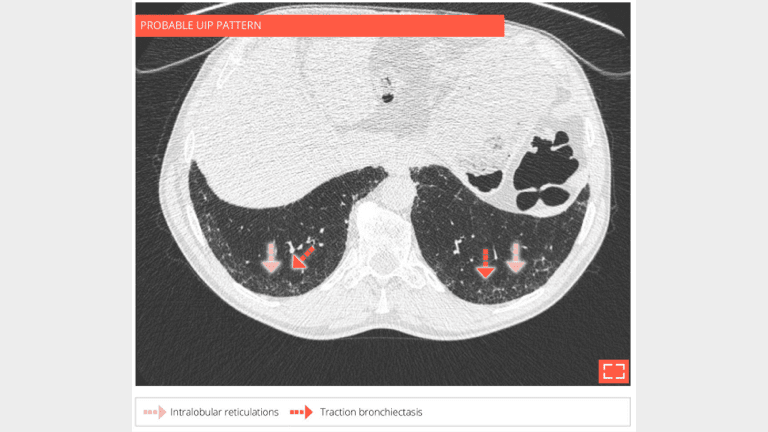
- Isolated and subtle subpleural intralobular reticulations and traction bronchiectasis of the 2 lower lobes.
- No ground-glass opacity or honeycombing.
4. Intralobular reticulations
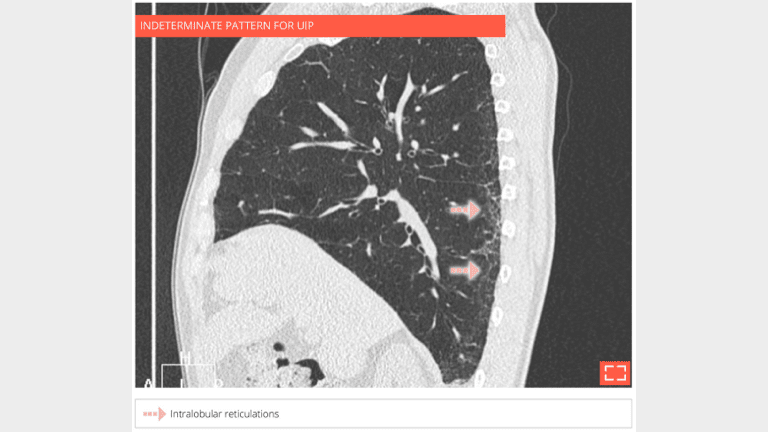
- Isolated and subtle subpleural intralobular reticulations.
- No ground-glass opacity or honeycombing or traction bronchectosis.
5. Intralobular reticulations
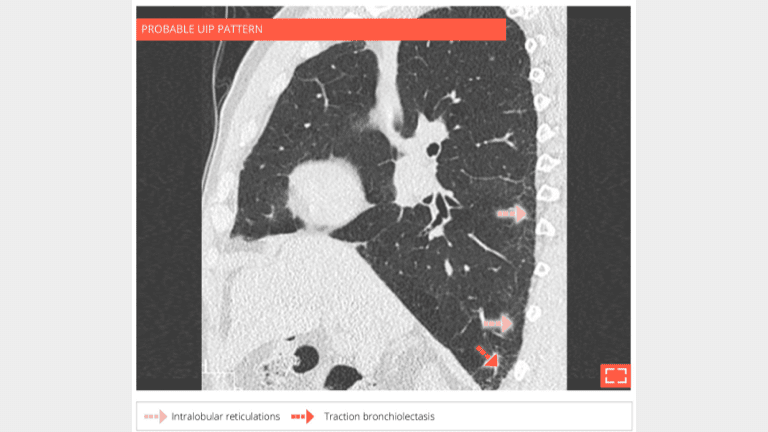
- Isolated and subtle intralobular reticulations, with traction bronchiolectasis.
- No ground-glass opacity or honeycombing.
