Elementary Lesions
Consolidation
Characteristics
Increase in pulmonary attenuation, generally homogenous
Obscuration of the margins of vessels, and airway walls
Air bronchogram could be present
Little to no degree of pulmonary collapse
Diagnostic Orientation
It is useful to distinguish between acute consolidation and prolonged consolidation (> 8 weeks)
In cases of prolonged consolidation, the following diagnoses can be considered:
pneumonic-type mucinous adenocarcinoma
pulmonary lymphoma
organising pneumonia (possible migration)
chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (possible migration)
exogenous lipoid pneumonia (low attenuation < -30 HU)
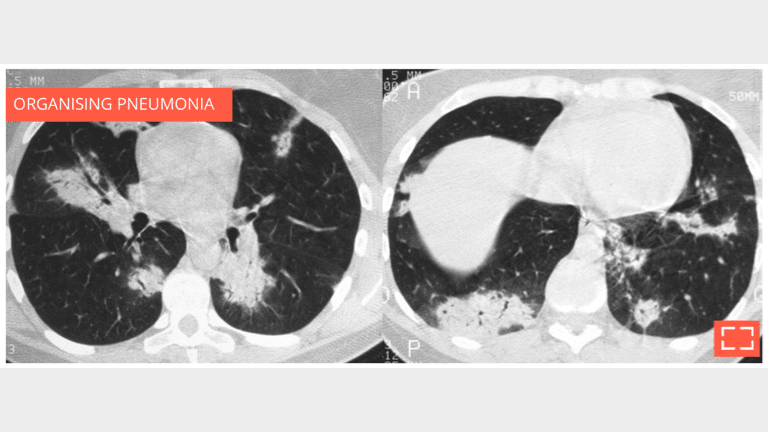
1. Consolidation
- Chronically evolving pulmonary consolidation (> 8 weeks) that is retractile with air bronchogram.
- The chronic nature of it means a fibroscopy with lavage must be performed.
- If results are negative, a transparietal lung biopsy should be suggested.
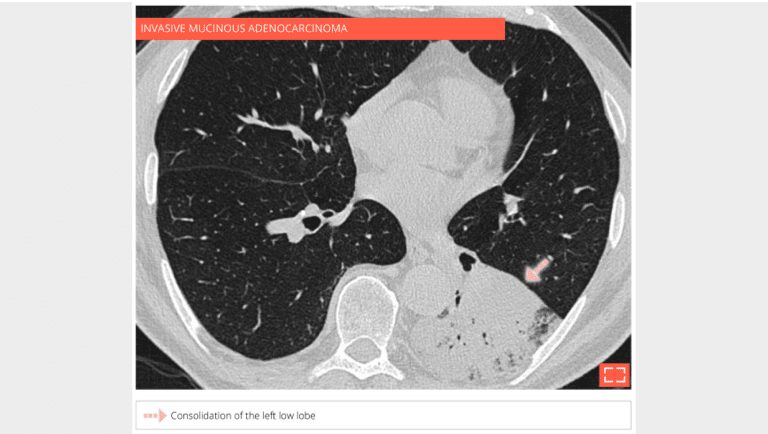
2. Alveolar consolidation
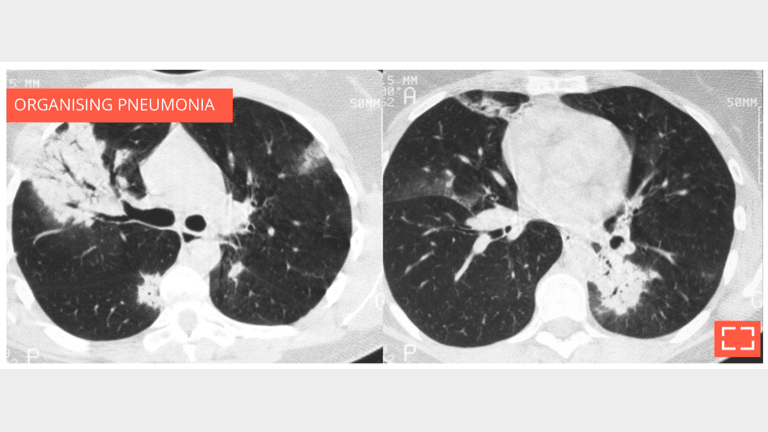
Bilateral subpleural alveolar consolidation with air bronchogram, in a patient with chronic cough.
- Note whether the foci migrate between the two scans, strengthening the argument for organising pneumonia.
3. Alveolar consolidation